emGUI basics II: Tweaking
This tutorial walks through the typical workflow of tuning a process inside the device.
- Assume that you have successful performed a Search and can see the device's tree.
- Assume that you are familiar with the platform and know which parameters, states and commands you wish to play with.
Setting the value of a parameter
Setting parameters arbitrarily is not recommended unless you know what you're doing. The motor or the vehicle may spontaneously accelerate. If you wish to have a more user-friendly experience with setting up a product, we recommend using some of our predefined plugins or scripts.
The simplest way: you can just click inside the contents column and edit the value in-line. Pressing Enter afterward writes the value to the device.
Double-clicking a parameter opens its dialog, where you can play with the value. You can dock the dialog inside the main emGUI window.
There are multiple ways how to change value:
-
Write your value to the text field:
-
You can specify the step value (if not predefined). Once the step value is set, you can use the
+and-buttons to increment/decrement the value by one step. The corresponding keyboard buttons and mouse wheel will also work: -
You can specify the min and max values (if not predefined). Once the min and max are set, you can drag&drop the slider for continuous value updates:
-
If they are defined, you can pick any of the presets:
After you change the value, this new value is not yet synced with the device. To set it, you need to click SET or press Enter.
For quick tuning, you can enable Autoset. With auto-set, the value will be auto-set and synced each time you change it:
For bulk value set, you can leave more of your values unsynced. They will be highlighted in blue. After your tweaking is done, you can select the Set value command from context menu (keyboard F2), for each modified variable. Or you can select Push subtree values on the folder's (or device's) context menu to push all modified values recursively:
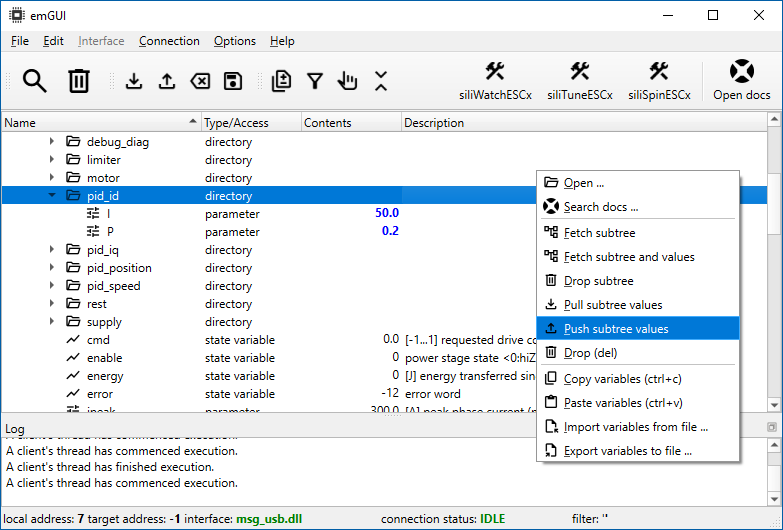
In all the variable dialogs, as well as in the content column, the special status of the value is indicated by a special color and style of its string:
- Bold: value has been changed from its default.
- Blue: value has not been synced with the device (marked inconsistent).
- Yellow: value has been imported from file/clipboard.
- : value has just been read from the device.
- : value has just been written to the device.
You can open multiple dialogs for the same parameter, prepare different values in each, and then use their set buttons for quick switching between the prepared values.
Newly set values will only stay in the device until reset. You need to issue the save command to make them persistent.
Executing an arbitrary command
Arbitrary command execution is not recommended unless you know what you're doing. The motor or the vehicle may spontaneously accelerate. If you wish to have a more user-friendly experience with setting up a product, we recommend using some of our predefined plugins or scripts.
To execute an arbitrary command, navigate to /commands folder. Double-clicking your command opens its dialog:
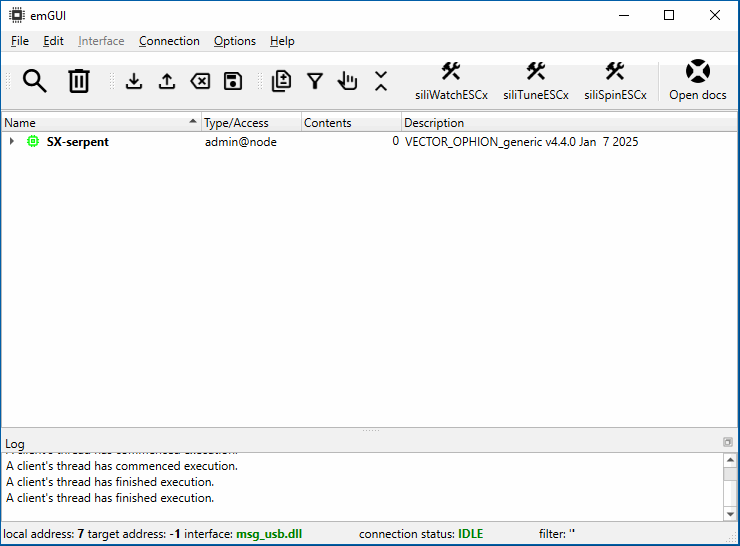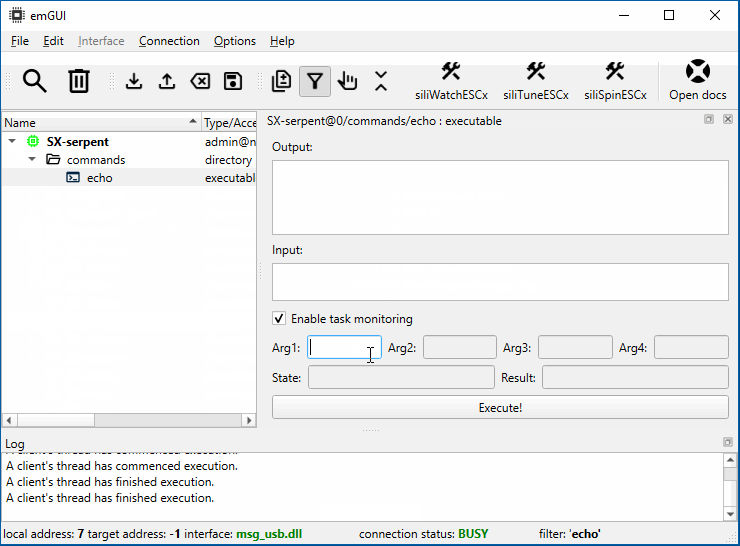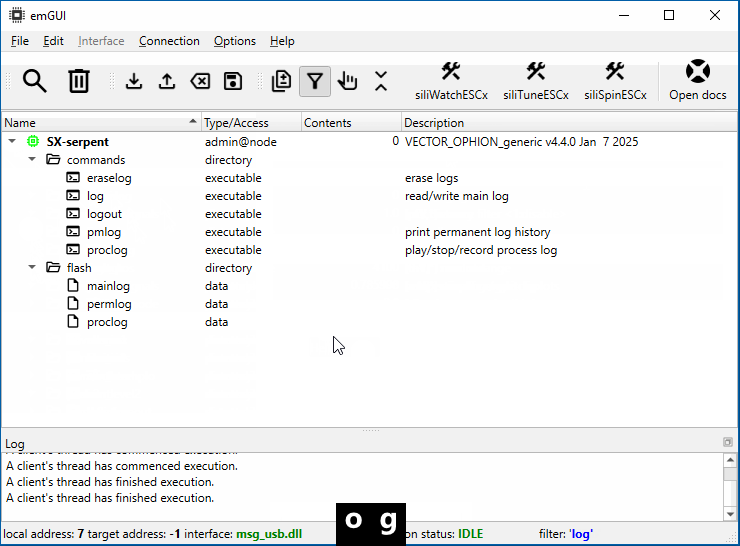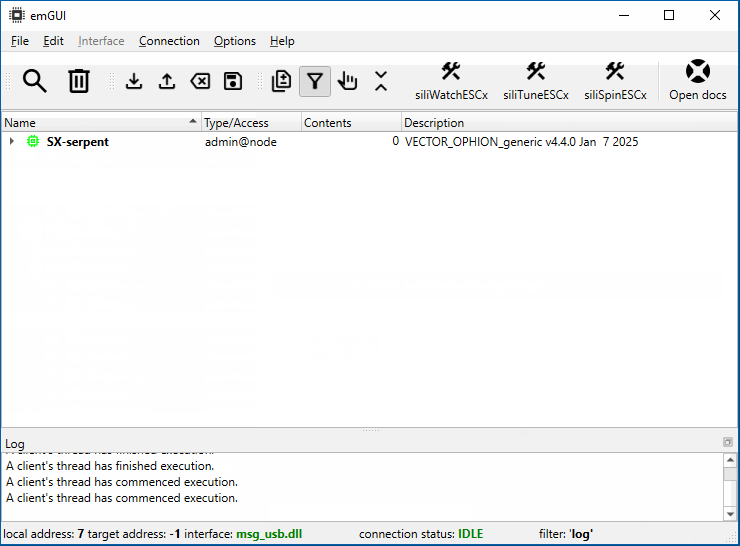
To execute, click the execute button. The execution status will be displayed in the State box. There are two ways (and their combinations) to exchange data with the command:
-
Arguments and result. The dialog contains 4 input string argument boxes and a single number result box. To append up to 4 input string arguments, fill them in the arguments boxes. The result of the command will be displayed after it finishes (usually, success is indicated by a zero return value). This example shows how to use echo command to mirror arguments into the standard output:
-
Standard input and output. The dialog consists of standard input and output edit boxes. To send a text input to the process, fill it in the standard input box before executing. This example shows how to load an internal script using script command:
-
Standard input and output with synchronization. If the command awaits input from you, the standard input box will be highlighted. This example shows the save command waiting for the user's confirmation:
You can open multiple dialogs for the same command, prepare input arguments in each, and then use their execute buttons for quick execution with different inputs.